Cutting-Edge Technical Presentations
Explore Wild River Technology’s collection of in-depth technical presentations covering the latest advancements in signal integrity, high-speed interconnect design, and measurement techniques. These expert-led sessions dive into practical challenges and emerging solutions across topics such as PAM4 modulation, electromagnetic simulation, crosstalk mitigation, and VNA-based analysis. Whether you’re developing next-gen systems or refining your design process, these presentations provide actionable insights to support your work at the forefront of high-speed electronics.
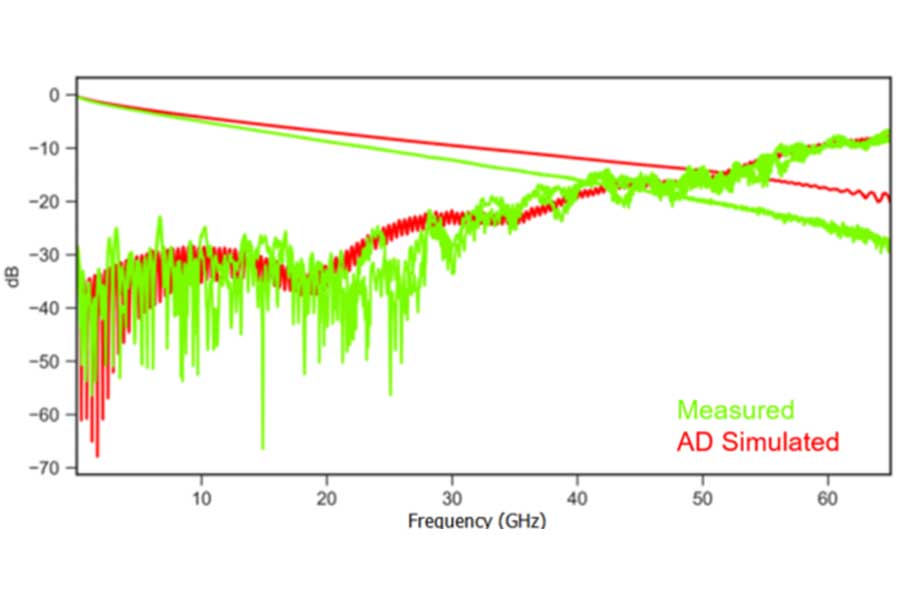
The “need for speed” in AI systems is driven by their requirement to process large data sets, both during training and application. Channel design is constrained by the balance between acceptable loss budget and the power consumed in equalization and error correction. Reducing channel loss can enable lower power or longer unrepeated channel lengths. Historically, high-speed serial links focused on material selection to manage attenuation. In 224 Gbps PAM4 systems, however, second-order factors like impedance variations, crosstalk, and power loss into cavities significantly impact the loss budget.
The “need for speed” in AI systems is driven by their requirement to process large data sets, both during training and application. Channel design is constrained by the balance between acceptable loss budget and the power consumed in equalization and error correction. Reducing channel loss can enable lower power or longer unrepeated channel lengths. Historically, high-speed serial links focused on material selection to manage attenuation. In 224 Gbps PAM4 systems, however, second-order factors like impedance variations, crosstalk, and power loss into cavities significantly impact the loss budget.
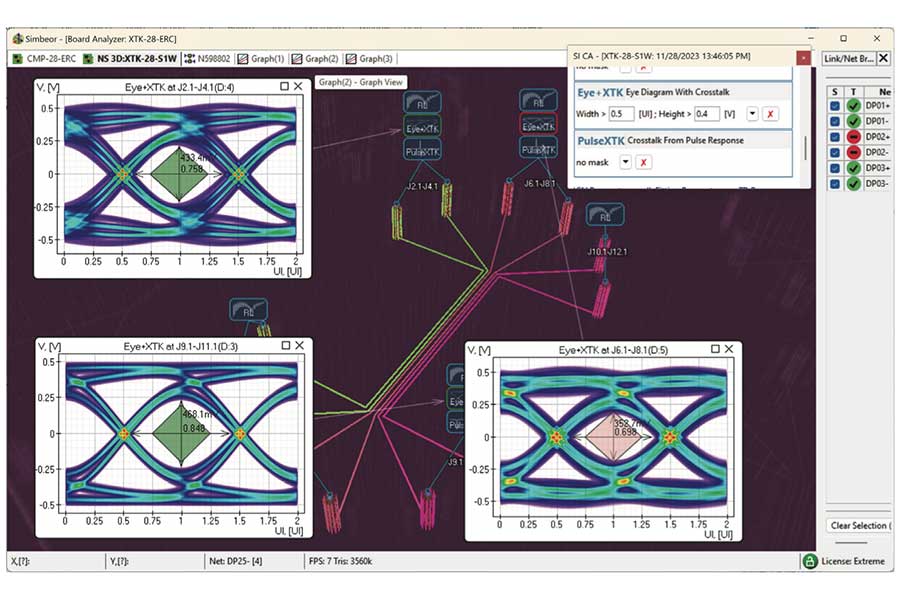
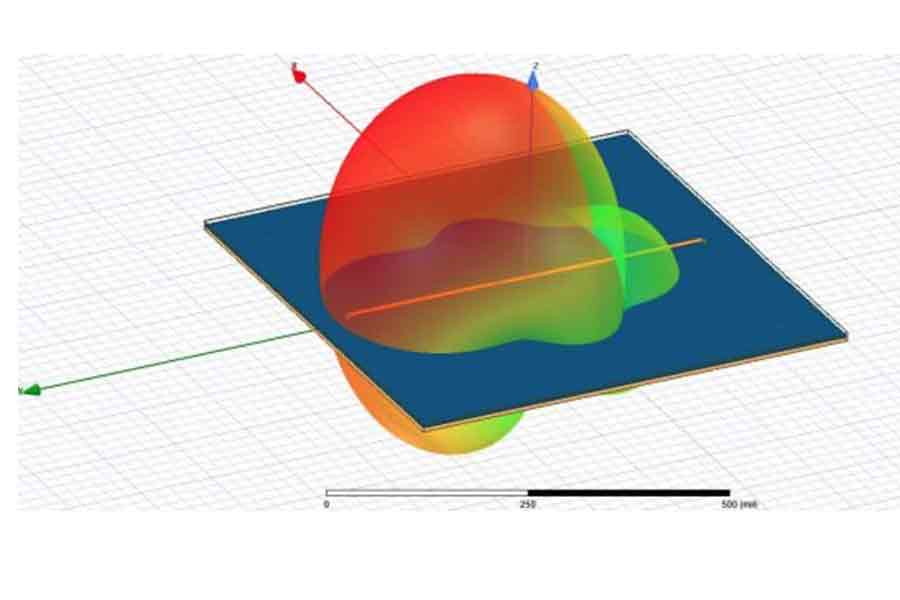
Crosstalk in PCB and packaging interconnects is unavoidable due to their open waveguiding nature, leading to signal energy leakage and exposure to noise from nearby and distant links via PDN structures. This tutorial aims to demystify crosstalk by explaining its mechanisms, quantification, and mitigation strategies. It details various crosstalk scenarios, visualized through power flow density derived from 3D EM analysis, and compares different quantification and mitigation techniques.
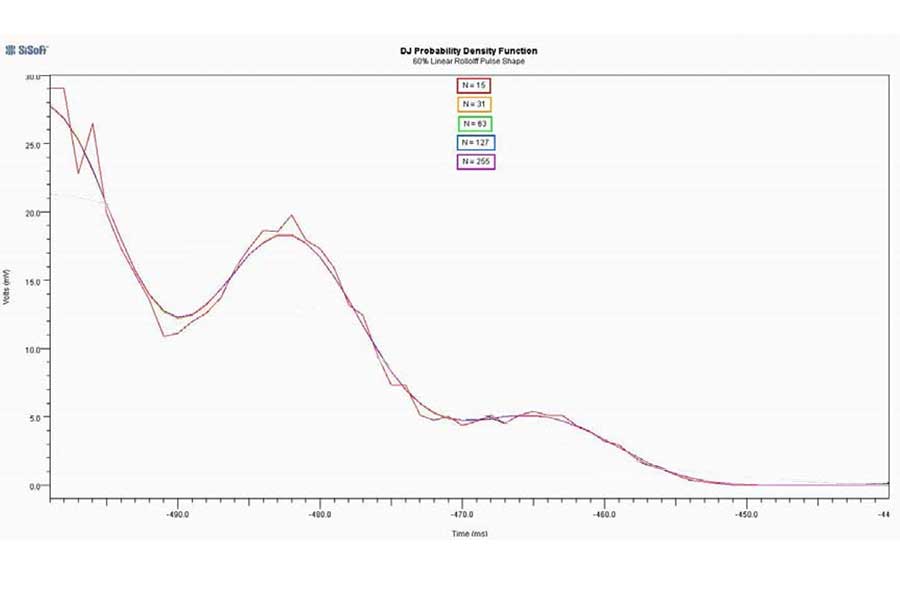
While Deterministic Jitter (DJ) is generally agreed to be peak limited, what is less clear is how rapidly its PDF decreases near that limit, especially when the DJ is due to crosstalk.
This paper addresses this and related questions by considering a class of responses which are similar to real system responses but are described by closed form equations. These responses can therefore be evaluated precisely at arbitrary times, allowing the tails of the jitter distribution to be explored in detail. The result is a clearer understanding of when the tails of a DJ PDF can resemble a Gaussian.
Crosstalk is unwanted noise from structures coupled to a signal link that degrade the useful signal and may reduce the data transmission rate and even cause complete link failure. All possible signal degradation effects, including the crosstalk, can be expressed with the balance of power.
This presentation discusses 400G test and measurement challenges. Specifically, it focuses on performing transmitter measurements of PAM4 modulated signals, discussing some of the pros and cons of using sampling oscilloscopes vs. using real-time oscilloscopes in making PAM4 measurements in the optical and electrical domains.
As backplane speeds rise, backplane/board/connector design is not getting any easier. In this presentation, we demonstrate new de-embedding techniques integrated into VNA firmware that make frequency-domain signal integrity measurements easier, more accurate, and less error-prone. We also present new tools to predict system response to arbitrary time domain signals. By implementing a “virtual” signal generator for multilevel PAM signals (NRZ, PAM-4, PAM-8, PAM-16), coupled with the impulse response of the measured S-parameters, eye diagrams are produced and updated in real-time.
As the industry plans it’s move to 112 Gbps, a number of signal integrity challenges must be addressed. Technology improvements will no doubt be part of the solution, but it is likely that evolving architectures will also be part of the solution.
This presentation discusses the industry trends driving the need to move forward to 112 Gbps; the electrical channels and electrical architectures anticipated to be part of the 112Gbps components, equipment, and networks; and finally, shares some analysis results based on some of these channels.
Al Neves discusses the challenges of attaining good signal integrity beyond 50 GHz. Topics include:
EDA Tools and Simulation Methodology What exactly is “Good SI” The “Alamo Strategy” for test fixture architecture The “Fabrication Hurdle” – What is it, how to get past it A new paradigm for critical SI connector / vendor working relationships Why program and project management gets in the way of 70 GHz SI
As signal speeds of complex electronics systems increase, component and system designs require more sophisticated, accurate, and user-friendly Electromagnetics based simulation tools. Fast, accurate, EM-based simulation is now an essential tool for any engineering team to achieve product release of high-speed connectors and PCBs. This presentation will discuss advances in Electronics simulation techniques including FEM and Transient Electromagnetic Simulation techniques; Automated Connector/Board Assembly Meshing/Analysis; Electromagnetics Based EMI/EMC Analysis; Crosstalk/Impedance Scanning; Integrated Electronics/Thermal Analysis (Multiphysics); High-Performance Computing; 3D Components, etc.
Topics:
For the Metrologist: Practical calibration methods suited for 3D-EM For the Signal Integrity Practitioner: Verification and assurance For the 3D-EM Modeler: Time domain processing and 3D-EM model development Tips:
Low frequency data is just as important as high frequency in both measurement and models Remember the basics: Start with the appropriate calibration and verify it Beware of the tools: Understand what they are doing Simulate to reduce design turns but measure to close the loop
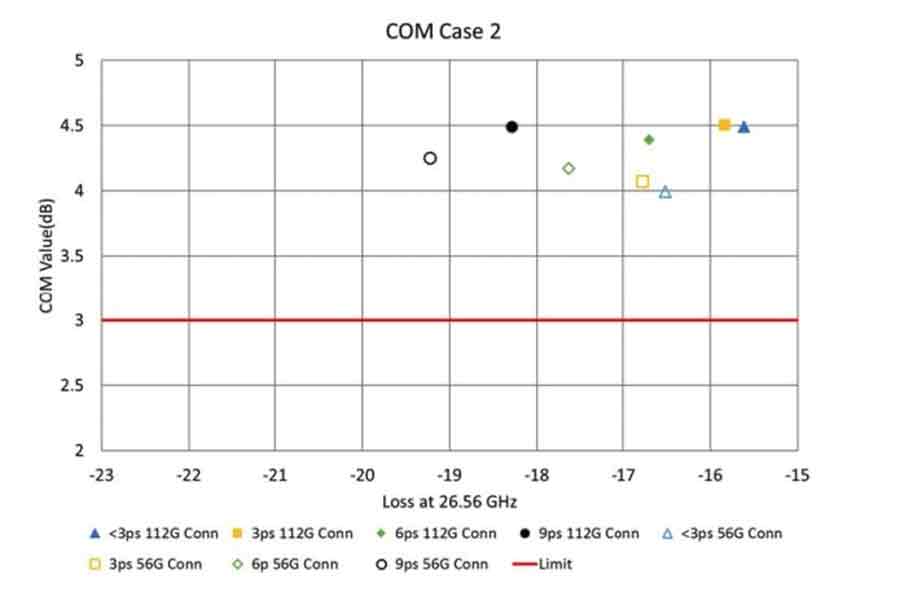
Robust Method for Addressing 12 Gbps Interoperability for High-Loss and Crosstalk-Aggressed Channels
This presentation addresses a new methodology for 12 Gbps interoperability that combines a concerted family of pathological channels, internal eye monitoring, and external EQ simulation tools, providing insight into an EQ optimization strategy that addresses the specific channel’s mix of crosstalk noise, jitter, and channel loss. This also provides a backplane designer the ability to configure a high-loss, crosstalk aggressed system. The method, combining co-simulation channel optimization, a reconfigurable channel platform, and receiver eye monitoring, has two key benefits; the separation of channel eye opening versus un-equalizable Deterministic Jitter (Dj), and the capability to map loss-crosstalk space for a particular SERDES channel pair, a new concept in SERDES interoperability evaluation. The method is described in detail, followed by relevant case examples using hardware specifically designed for this endeavor. Finally, we compare eye monitor results with the original co-simulation, validating the method.
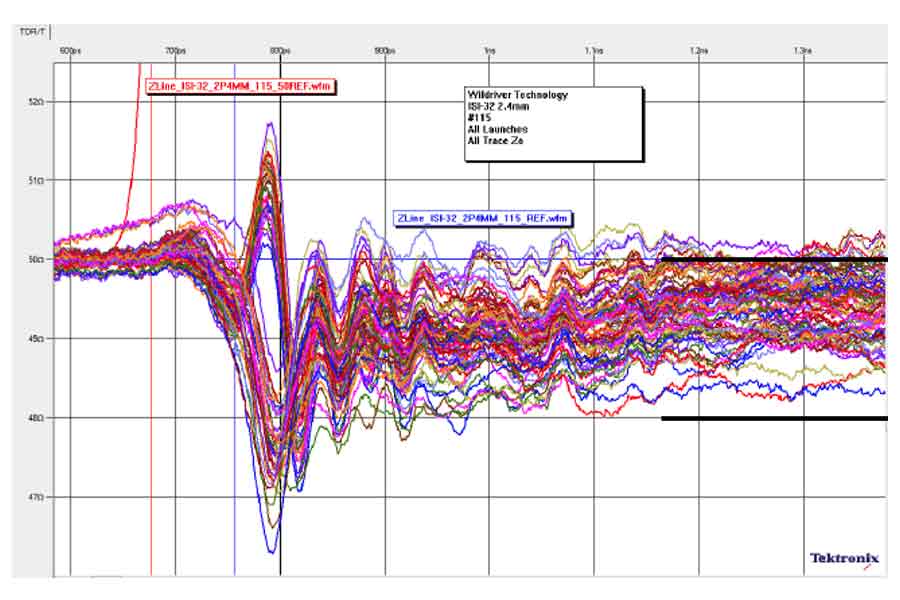
Design of interconnects on PCBs for 6-10 Gb/s data rates requires electromagnetic models from DC up to 20 GHz. Manufacturers of low-cost FR-4 PCBs typically provide values for dielectric constant and loss tangent either at one frequency or without specifying frequency value at all, that is not acceptable for the broad-band models. A simple and practical methodology to extract frequency-dependent dielectric parameters on the base of correlation of measurements and simulations is proposed. A board with 30 test structures has been built to validate the extraction methodology and to verify possibilities to predict interconnect parameters with the electromagnetic analysis.
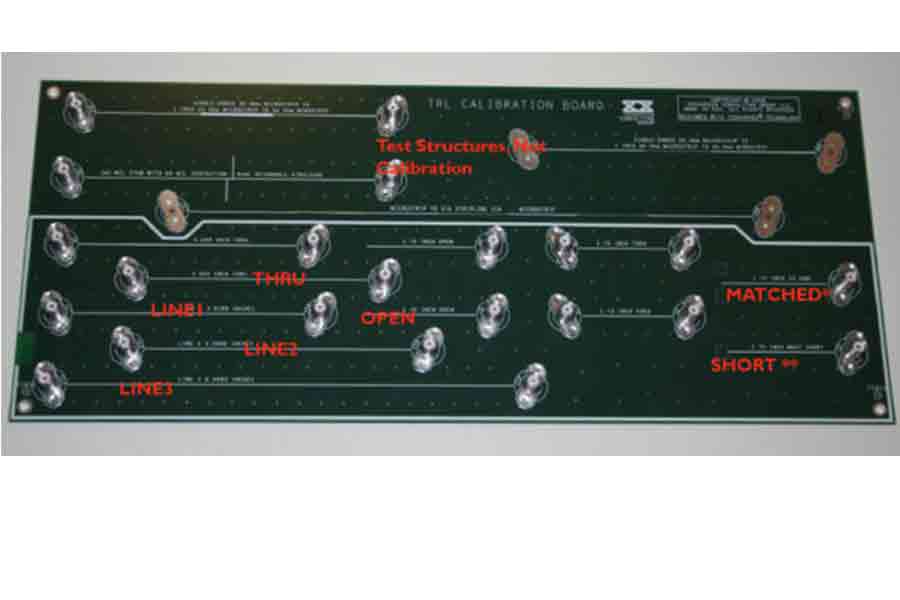
This presentation explores essential calibration and de-embedding techniques used in high-speed measurement systems. Topics include foundational concepts, how to select the appropriate measurement approach, and practical examples of SOLT and TRL methods. Attendees will also learn how to create a TRL calibration kit, assess calibration accuracy, and compare results with 3D field solver-based measurements.