Insights & White Papers
Explore our collection of technical white papers covering advanced topics in high-speed signal integrity, interconnect modeling, and measurement methodologies. Our research-driven insights help engineers tackle challenges in channel compliance, jitter analysis, electromagnetic extraction, and high-speed serial data transmission.
This paper analyzes second-order design features using precision measurements of test vehicles and digital twins. We propose a metric-driven methodology based on AI/ML to determine relevant parameters for simulating anisotropic behavior that matches both time and frequency domain measurements.
This paper analyzes second-order design features using precision measurements of test vehicles and digital twins. We propose a metric-driven methodology based on AI/ML to determine relevant parameters for simulating anisotropic behavior that matches both time and frequency domain measurements.
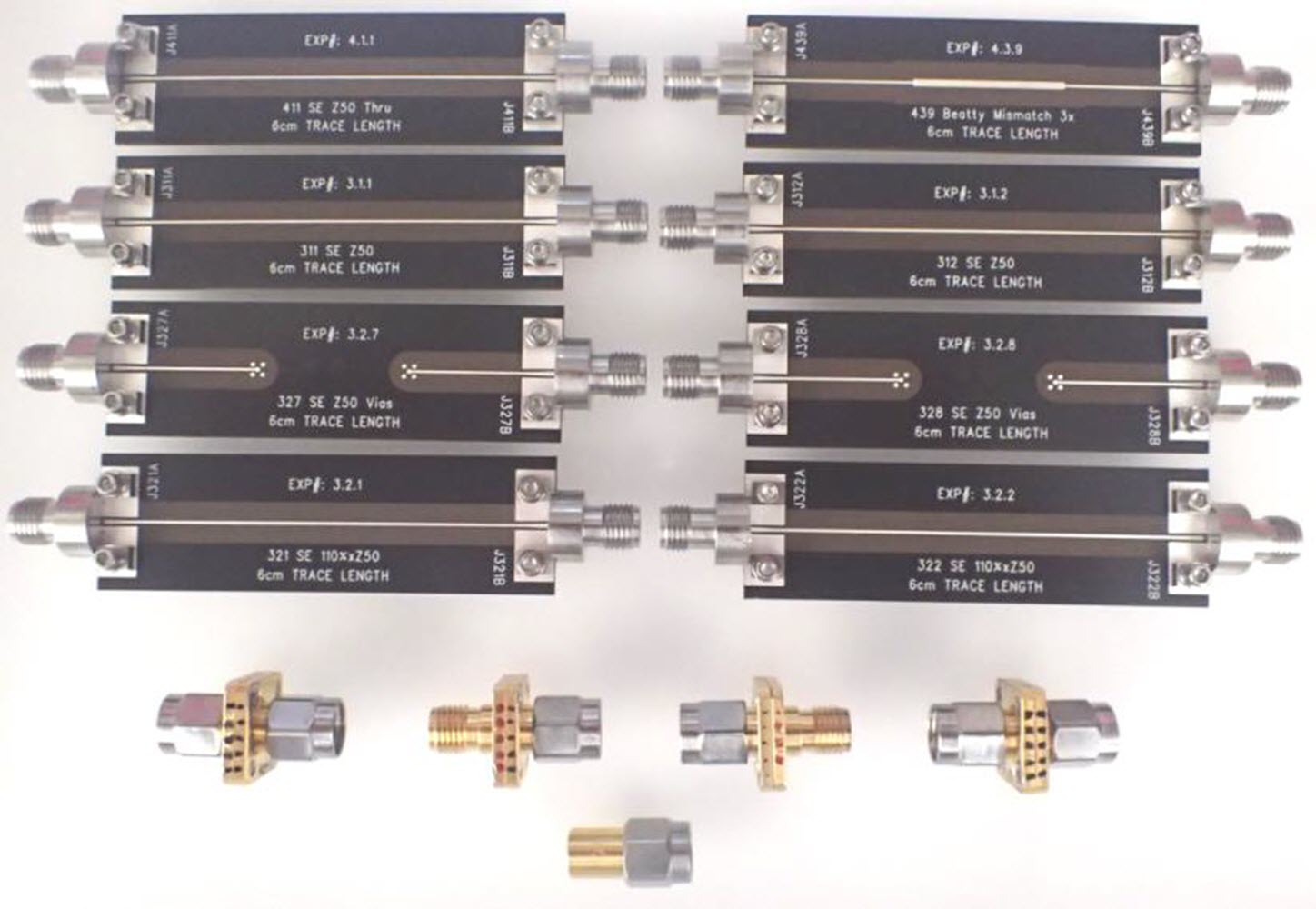
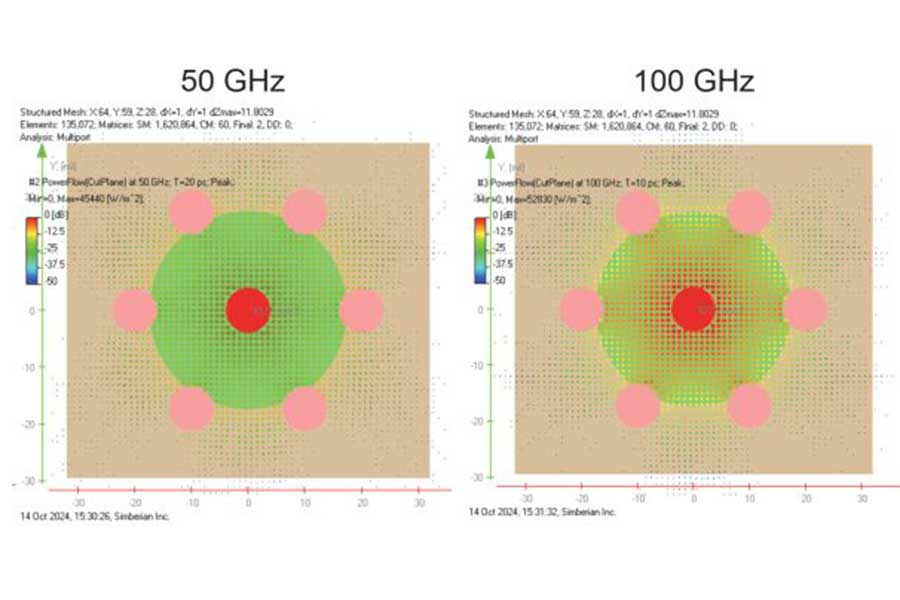
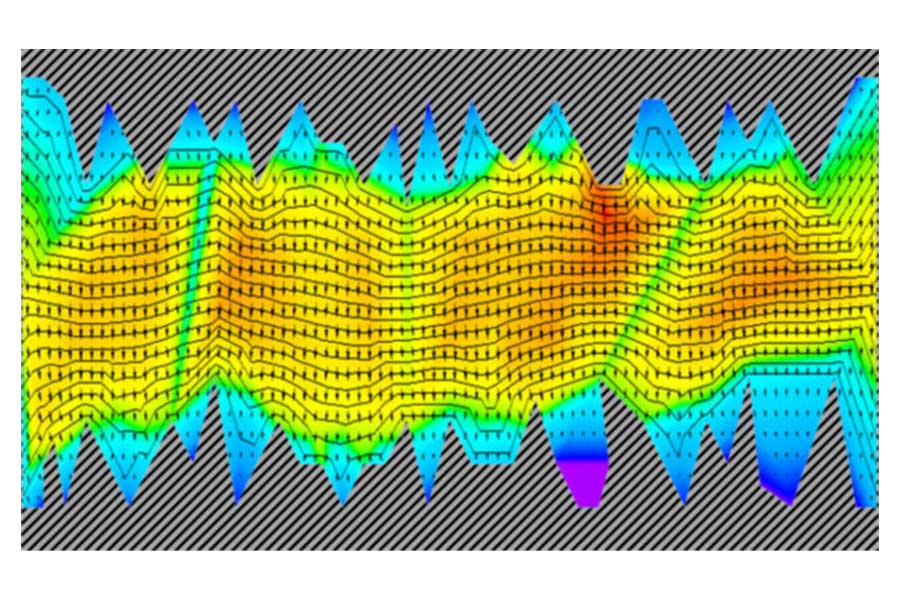
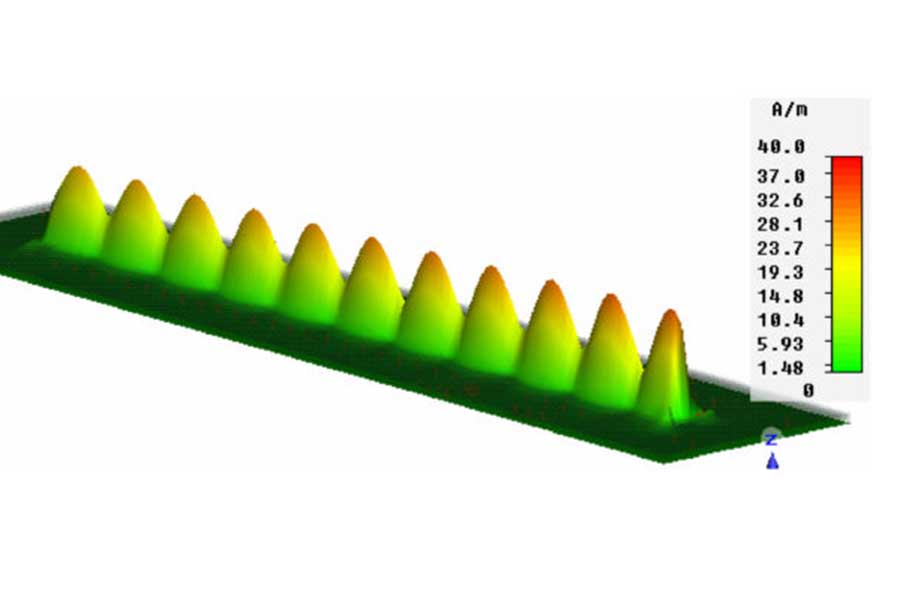
This work presents a novel approach of PCB vias design and optimization for 112 and 224 Gb applications. As data rates go up, vias are becoming increasingly important for signal integrity yet increasingly challenging in successful real-life implementation due to the necessity of tighter control over via’s properties such as signal reflection, dissipation, and crosstalk at higher frequencies. Vias design is often becoming the limiting factor for the ultra-high-speed channel performance. To make matters worse vias electrical performance at high frequencies is often dominated by PCBs and Package manufacturing variations. We explore the physics of vias – conditions and metrics for localization within single-mode bandwidth up to 120 GHz. A novel approach is introduced to design for robustness against manufacturing variation, stackup adjustments due to copper density or multi-sourcing support. We demonstrate a practical design methodology prioritizing low sensitivity to these factors while meeting the low reflection criteria. The paper demonstrates some insights into the practical discrepancies between theoretical designs and manufactured vias, bridging the theory with realities.
In the GB/s regime, accurate modeling of conductor loss and phase delay is a precursor to successful high-speed serial link designs. In this paper, a practical method to model effective permittivity and phase delay, due to conductor surface roughness, is presented. By obtaining the dielectric and roughness parameters, solely from manufacturers’ data sheets, phase delay and effective permittivity can now be easily predicted. Detailed case studies and several examples test the model`s accuracy.
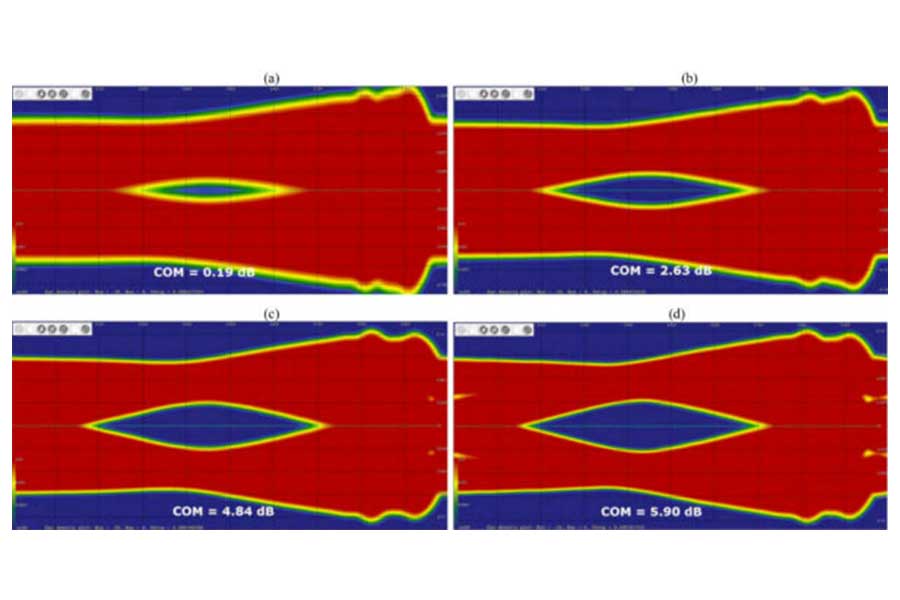
In this paper, we analyze the computational procedure specified for Channel Operation Margin (COM) and compare it to traditional statistical eye/BER analysis. There are a number of differences between the two approaches, ranging from how they perform channel characterization, to how they consider Tx and Rx noise and apply termination, to the differences between numerical procedures employed to convert given jitter and crosstalk responses into the vertical distribution characterizing eye diagrams and BER. We show that depending on the channel COM may potentially overestimate the effect of crosstalk and, depending on a number of factors, over- or underestimate the effect of transmit jitter, especially when the channel operates at the rate limits. We propose a modification to the COM procedure that eliminates these problems without considerable work increase.
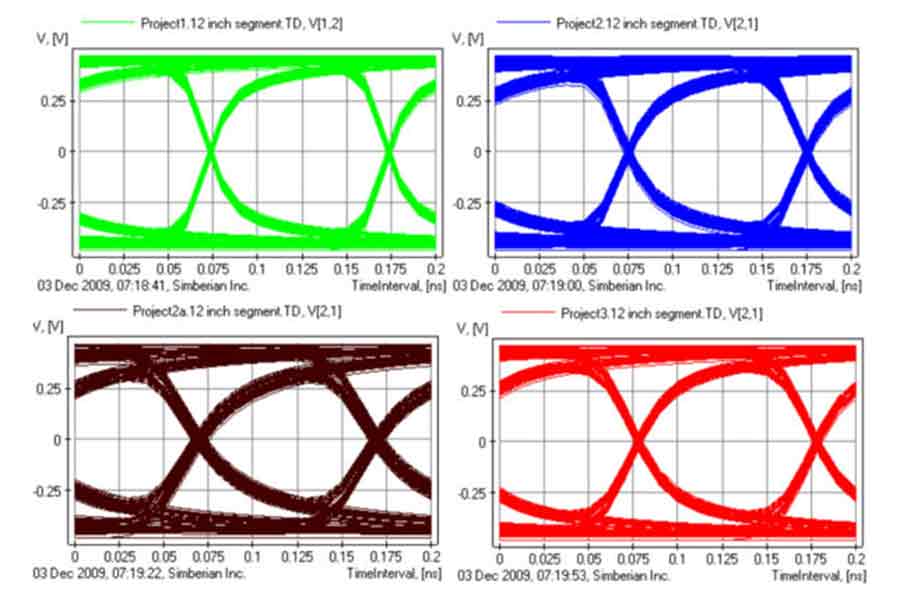
As serial link speeds increase, systems become more “Stressed”. Loss, low probability deterministic jitter, crosstalk aggression from densely packed signal nets, via and connector impedance and associated resonances, and package and power delivery issues all add their own jitter density function, resulting in a net jitter picture that is inherently complicated. This paper represents a rigorous and practical crosstalk analysis of 10Gbps and higher serial data transmission systems, which will begin at pre-layout 3D EM extraction, continue with the material parameters identification and post-layout analysis and end with direct jitter measurement and separation. We believe this is one of the timeliest of topics in signal integrity at the present time.
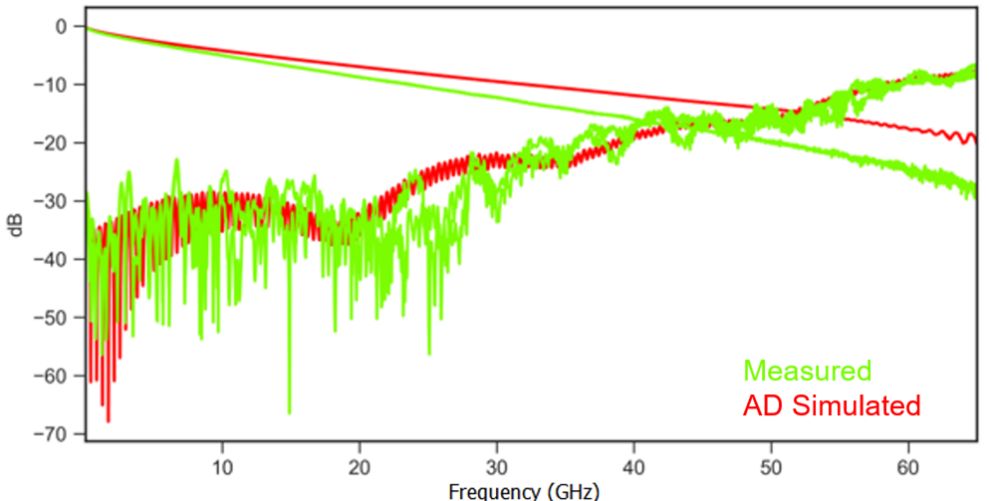
Traditional frequency-domain 3D electromagnetic modeling methods, originally applied to low-bandwidth microwave designs, face significant challenges at today’s data rates above 20 Gbps—particularly with causality and passivity violations. To address these limitations, a new inherently passive and causal time-domain oriented approach is presented. This method offers clear advantages for high-speed baseband-NRZ backplanes, interconnects, and general board design in digital systems. The discussion highlights the importance of selecting the correct loss model, with results validated against actual measurements up to 20 GHz using a purpose-built test board.
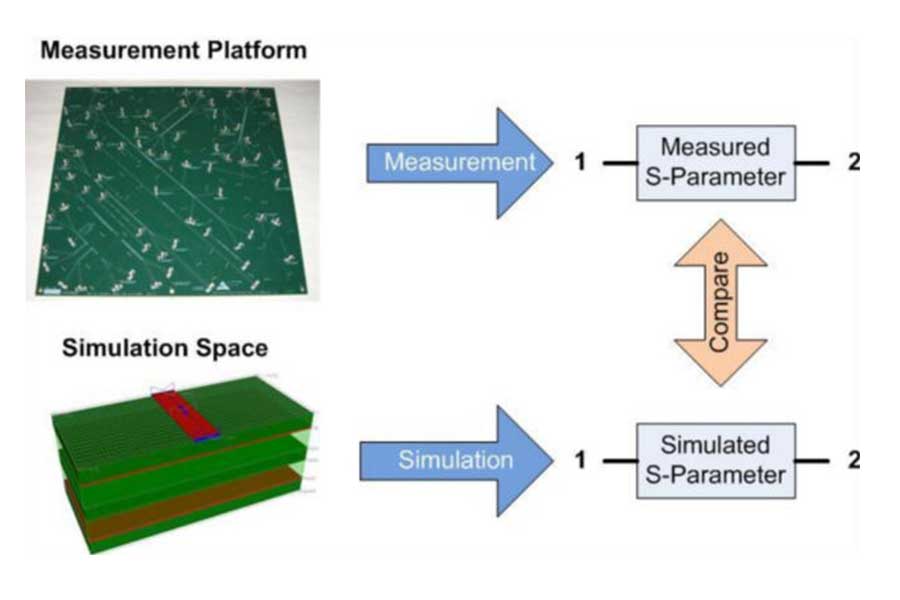
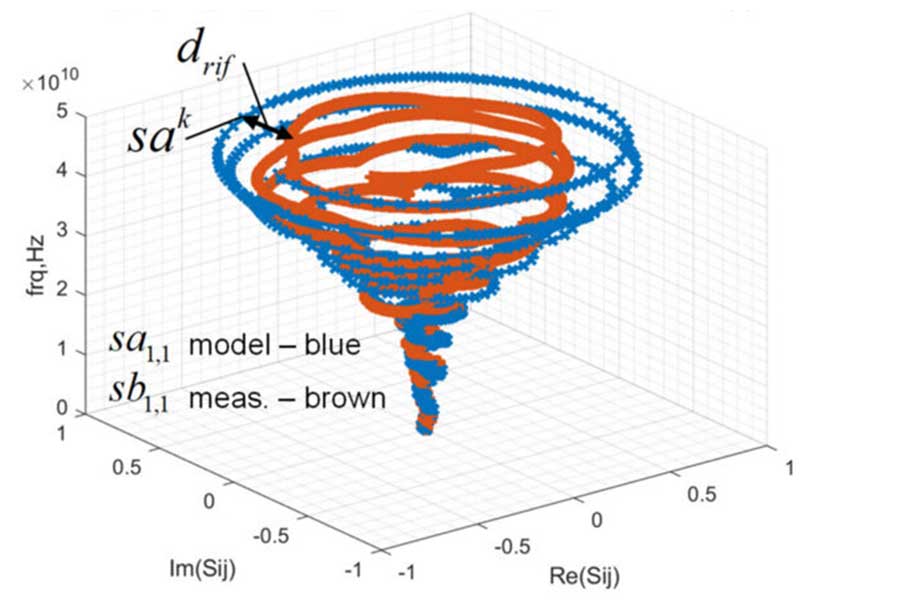
A new similarity measure for two sets of S-parameters is proposed. It is constructed with the modified Hausdorff distance applied to S-parameter points in 3D space with real, imaginary and normalized frequency axes. New S-parameters similarity measure facilitates automation of the analysis to measurement validation, comparison of models and measurements obtained with different tools, as well as finding similar S-parameter models or similar elements within S-matrices.
A novel method for extraction of dispersive dielectric parameters to 50 GHz is proposed. The method doesn’t require advanced de-embedding, and is based on correlation of measured and simulated generalized modal S-parameters of a line segment. First, VNA measurements for two line segments are made and used to compute generalized S-parameters of a difference segment. Second, 3D full-wave model of the difference segment with conductor model with roughness is used to identify the dielectric properties. We finalize the paper with the derivation of dielectric models for low-cost FR4-type and for expensive low-loss high-frequency materials. The advanced models can be used for practical electromagnetic analysis of interconnects for the 6-100 Gb/s realm.